In this blog, we will talk about the effects of waterlogging on plants, the different types of plants that are more vulnerable to this stressor, and the possible ways to control this phenomenon.
Plants die in waterlogged soil because it deprives them of oxygen and light.
The roots of the plant will no longer be able to absorb nutrients and water because there is too much water in the ground.
The roots of the plant are unable to absorb nutrients and water because there is not enough soil in the ground. So, continue below to learn more about water log conditions with plants
What is waterlogging?

Waterlogging is the saturation of soil with excess water. The pressure exerted by the standing water prevents oxygen from entering the soil and allows anaerobic bacteria to thrive, causing a loss of plant life.
It is difficult for plants to survive in a submerged environment because they are not able to absorb enough nutrients through their roots.
Furthermore, these plants suffer from stress that damages the cellular structure and can lead to cell death or prevent new growth.
Waterlogging is also caused by a lack of the soil’s ability to absorb and retain water. The roots of plants absorb oxygen through their fine tissues to support cellular respiration and allow plants to perform photosynthesis.
Plant waterlogging can be a result of high albedo, low albedo, or a combination of both. This creates an environment in which the water evaporates much faster than it can be absorbed. As a result, the plant is forced to transpire and emit water vapor into the atmosphere.
The albedo of the soil plays a large role in determining how quickly plants will be able to absorb water from it.
Albedo refers to how reflective or absorptive an object is. The higher the albedo, the more ultraviolet rays will be reflected (and thus how quickly water will evaporate).
The albedo of different types of soil varies considerably. Fertile soil is likely to have a higher albedo than sandy soil.
Why do plants die in waterlogged soil?
Plants need oxygen to grow, and waterlogged soil does not supply enough for them to survive.
The roots of plants will not be able to anchor themselves in waterlogged soil, which can make the roots rot and the plant die.
If a plant is trying to get as much oxygen as possible in order to stay alive, it will use up all of its energy reserves and die before it can produce
How Long Can Plants Survive Waterlogged Areas?
Plants that are waterlogged at home can be a result of floods, burst pipes, or leaks. What’s more, this can happen in the car for those who live in coastal areas.
The good news is that plants don’t need to be rescued from their soggy homes by giving them a drink.
Instead, it is best to let the soil dry out and then use a hairdryer on low heat to speed up the process.
Some plants, like cacti and succulents, are particularly resilient, but not all plants. If you want to save the plant, what you need to do is repot it into semi-dry soil and stick with it for a few weeks.
Some plants will recover from the shock of being moved; others won’t.
Why do plants die under waterlogged conditions?
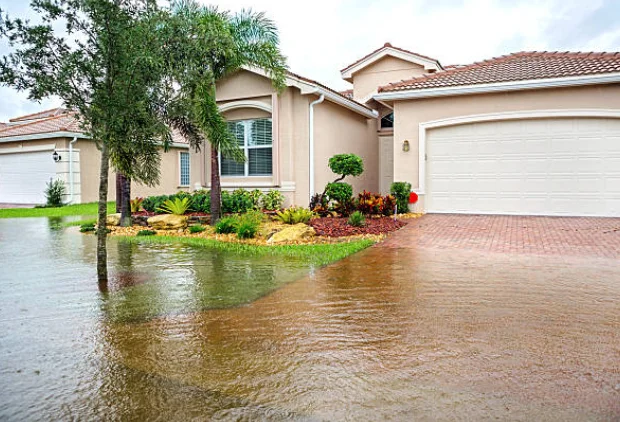

Waterlogged conditions are usually caused by heavy rains and flooding.
The soil gets saturated with water, preventing the plants from taking up oxygen.
Plants need oxygen to survive. When there is too much water in the soil so that it cannot be drained out, plants will die.
This happens because plants take in oxygen through their roots, but when there is too much water in the soil, they cannot get enough oxygen to stay alive.
This may also happen when a water source is left uncovered. Wet leaves and other organic materials create perfect breeding grounds for bacteria that are harmful to plants.
These bacteria quickly break down the organic materials, producing toxic gases and enhancing the levels of oxygen in the soil.
When a plant dies, it can create anaerobic conditions that will harm other plants.
Does waterlogged soil affect plant growth?
Soil is a complex, dynamic system. It is composed of many different types of soil. Soils are made up of minerals, organic matter, and water. The type of soil determines how it will react to water and other substances.
Waterlogged soil can affect plant growth in two ways:
1) Waterlogged soils are usually low in oxygen, which reduces the amount of air that plants need to grow.
2) Waterlogged soils often have high amounts of salt that can make the soil toxic for plants.
Why do plants need air?
Many people think that plants need water to grow, but this is not true.
Plants don’t need water to stay alive. The roots of the plant absorb all the water they need from the ground instead of from rain or sprinklers.
So why do plants die in wet soil? Well, not all the roots can draw enough air into the soil because of how compact it is from rain and runoff.
Their leaves also might rot when they’re exposed to moisture and humidity because they’re not getting enough oxygen.
Wet soil can also be a breeding ground for pests like root-knot nematodes, which can destroy plants’ roots and make them less effective at absorbing water.
How Do You Save a Waterlogged Plant?

Plants need oxygen to grow and thrive. When the soil is saturated by water, plants cannot take in enough air for their roots or leaves.
One way to save a waterlogged plant is to use a pot with drain holes and clear away the excess water from the plant’s container.
The excess water can be disposed of by tilting the pot and letting it drain out, or by using a hose to rinse off the excess water.
Soil that is too wet cannot be used for plant growth. Waterlogged soil will not hold on to nutrients or retain water.
Another way to correct this problem is to use a pot with drain holes and remove excess water from the plant’s container.
The excess water can be disposed of by tilting the pot and letting it drain out, or by using a hose to rinse off the excess water.
What causes waterlogging, and how can we avoid it?
When plants are subjected to this condition, they will start to die and decline in health.
Waterlogging is caused by a lack of drainage; the best remedies for it are digging holes and trenches and installing drains.
Waterlogging is a condition that causes the soil to be saturated with water. The water table rises when there is heavy rain, and the plant’s roots are continuously in contact with it.
This happens when there is poor drainage in the area and the soil is not able to drain. .Waterlogging results in a buildup of water in the soil.
This causes the plants’ roots to remain wet for prolonged periods, which weakens their ability to take up nutrients such as nitrogen and oxygen from the soil. Root damage can result in stunted growth, wilting leaves, root rot, and eventually plant death.
Waterlogging can also be linked to soil compaction. This happens when there is too much traffic on a piece of land and the soil becomes compacted from the weight of human or animal traffic.
How can I improve clay soil?
You can improve your clay soil by doing the following:.
- The soil must be able to absorb water or else the roots will die
- Wet soil does not receive air exchange, and this makes it hard for plants to survive In a wet soil environment, plants are deprived of oxygen because the soil is unable to absorb water.
This leads to plant death as the roots are not getting sufficient oxygen.
Furthermore, wet soils do not allow for air exchanges, which limits the number of dissolved gases that come from deep in the ground and reach higher levels in the atmosphere.
This deprives plants of crucial elements such as carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide, which they need for photosynthesis.
What does water on the leaves prevent?
Plants need to receive carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide for proper growth and photosynthesis. Plants do not get these essential elements in wet soil environments, which leads to plant death.